Views: 77
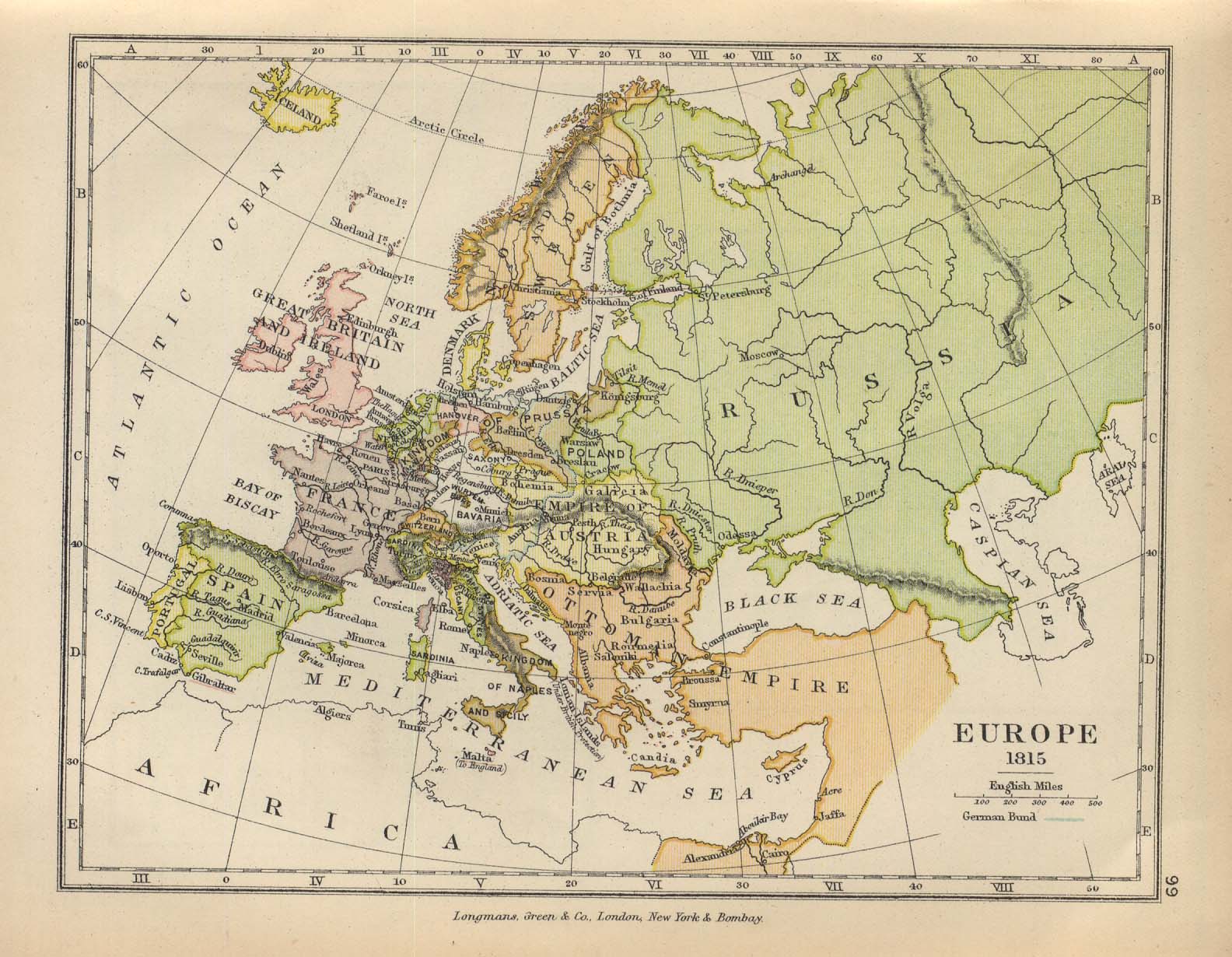
The period from 1462 to 1815 is of special importance for the history of Russia and the Russian people as well as for the history of Eurasia for at least five good reasons: 1) Russia became modernized according to the European pattern; 2) Russia became liberated from the foreign occupants; 3) The Russian people became territorially united into a single national state; 4) Eurasia experienced Russian territorial expansion in all directions from its original administrative center in Moscow and later St Petersburg; and finally 5) Russia as the mighty empire became a member of European concert of Great Powers and even the most powerful state in Eurasia after the Napoleonic Wars.
The period started with the realm of Ivan the Great (Ivan III Vasilievich, 1462−1505) to be ended with the final decisions of the Congress of Vienna in 1815. That was the Grand Duchy of Moscow, known as Moscovy, as the state created by the Grand Dukes of Moscow in north-east Russia to be destined to commit two great historical tasks: 1) To recover the territories lost to the Swedish, Polish, Lithuanian, German, Ottoman, and Mongol/Tartar occupants (in the west and south), and 2) To expand Russian authority across North Asia (Siberia) up to the Pacific Ocean. However, it has to be noticed that in 1462 the crucial aspect of Russian participation in international relations was, in fact, zero as the state was almost in absolute isolation from the rest of the world. In other words, Moscovy Russia was in the mid-15th century isolated from almost all contact with the outside communities simply by the hostility of its direct neighbors. In particular, Moscovy Russia was not in a position to share in both scientific and cultural issues of Europe, and from this perspective became relatively backward compared with especially West Europe. However, lesser than four centuries later, in 1815 Russian Empire became the most powerful participant in European politics and international relations.
The territories of the Russian people ruled from Kiev (the Kieven Rus’) have been split due to the Mongol occupation in the mid-13th century followed by the occupation by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania into two parts: eastern and western. The eastern lands were under the authority of Mongols while the western territories became crucial parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (including Kiev) to be after the Lublin Union of 1569 (signed between Poland and Lithuania) incorporated into the Kingdom of Poland. Nevertheless, under the shadow of Mongol overlordship, the Grand Duchy of Moscow succeeded to dominate its Russian neighbors and finally threw off the Mongol/Tartar yoke.
The growing power of the Grand Duchy of Moscow was gradual and finally obtained political independence from the Mongols/Tartars under the rule of Ivan the Great in 1480. The political-military power of Moscovy was first exerted eastward and later southeastward. The northern territories of Novgorod have been the next (in 1478) followed by Pskov (1510). Nevertheless, one of the most successful and important conquests by Moscovyte Russia (from 1547 the Empire) was in 1552 when the Khanate of Kazan became subjugated to Russian rule. Consequently, this conquest opened the way for Russia to advance across the Urals and into Siberia. Subsequently, the Tartar Khanate of Astrakhan became conquered in 1556 which gave Russia control of the Volga and all ways to the Caspian Sea.
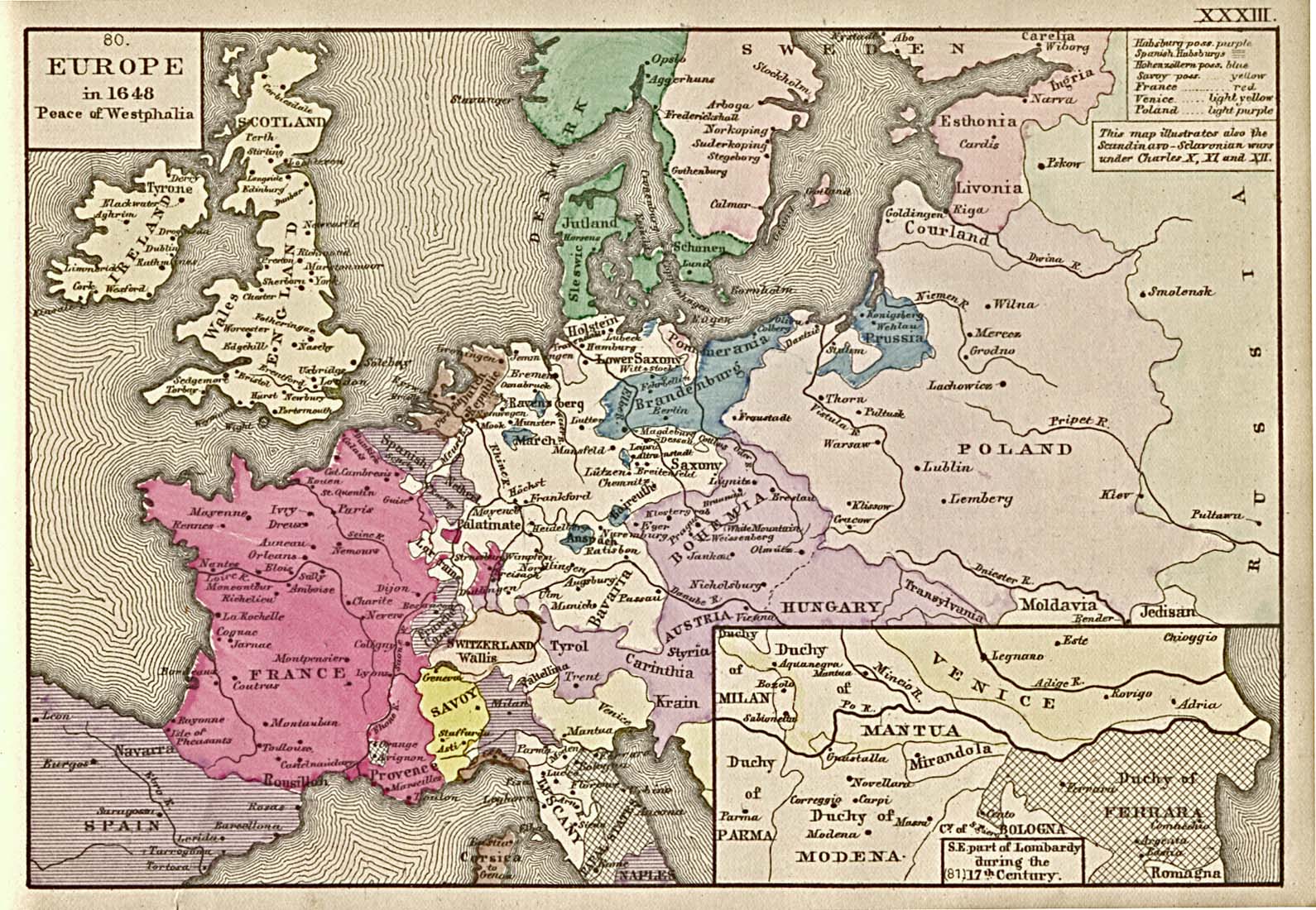
However, in the second half of the 16th century, Russia experienced certain setbacks during the Livonian War (1558−1583) under Ivan IV the Terrible (1533−1584) as this debilitating war for a quarter of a century on the Polish-Lithuanian and Swedish frontiers was, in principle, not successful for Russia. Moscow was in the year 1571 even sacked by the invading army of the Tartars from Crimea.
Nevertheless, Siberia became the biggest challenge of the Russian territorial expansion at the turn of the 17th century. Originally, it was the fur trade that involved Russian merchants in the unknown and rarely settled territory of Siberia (that was, in fact, terra incognita). Russians finally reached the coast of the Pacific Ocean in 1639 followed by the establishment of the holds (like the Americans did in the Wild West). In essence, the plenty of Siberian rivers very much facilitated fast exploration that became soon inforced by strategic forts and trading posts. In fact, all of Siberia except the Amur region became acquired from native primitive peoples (Tungusy, Ostyaks, Lamuts, Koryaks, Chukchi, Yakuts, Evenki…) – the Amur was annexed from China in the 1650s but was given up in 1689 according to the Treaty of Nerchinsk with China. Parallelly, the opening of the Volga trade route led to the fast growth of the silk trade with Persia/Iran via the Caspian Sea.
After the Time of Troubles in Russian history, which followed the deaths of Ivan the Terrible (1584) and Boris Godunov (1605) in 1613 Michael Romanov became elected Russian Tsar/Emperor – the founder of the Romanov ruling dynasty (1613−1917). The Romanovs in the 17th century turned their attention to the recovery of West Russia which was for centuries under the Lithuanian-Polish occupation. At the beginning of this campaign, there were certain losses which have been caused mainly by the internal political chaos and disunity of the earlier period known as the Time of Troubles. However, important gains have been done from 1640 to 1686. For instance, in 1667, Kiev and the mid-Dneper territories were gained. The Cossacs of the lower Dnieper led by Bohdan Khmelnytsky voluntarily accepted the Russian rule instead of the Polish Catholic yoke in 1654, and their land of Zaporozh’ye, therefore, became since that time claimed by Russia.
In the second half of the 16th century and throughout the 17th century, Russian colonization spread across the Oka River in the south while some Eastern Slavs migrated from Poland into the forest-steppe zone. At the time, several towns in this zone started their existence as borderland outposts like, for instance, Orel (1564), Voronezh (1586), or Kursk (1586). Nevertheless, at the time, isolation from Europe was the focal problem for Russia until the time of Tsar Peter the Great (1682−1725). On one hand, there was a huge demand for different products from the Russian forest and land by West Europeans but, on the other hand, Russia was unable to profit from such demand for the very physical reason that Poland-Lithuania, Sweden, and the Ottoman Empire simply blocked both oversea and overland links with Europe. It is true that the Brits for commercial purposes succeeded to open up a very dangerous northern route to the White Sea via the Barents Sea and that Russian Tsar Ivan the Terrible established the seaport of Archangel in 1584. However, Archangel as the outlet for the export of Russian products to Europe was workable only during the summertime for a few months. For several reasons, therefore, Russian Tsar Peter the Great accepted as his focal national aim in foreign policy to break through to the shores of the Baltic Sea and consequently, took from Sweden Estonia and Livonia after the Great Northern War (1700−1725) which, in fact, Swedish King Charles XII started against Russia. The seaport of Riga became acquainted and a new Russia’s capital on the Baltic Sea was established in 1703 – St Petersburg. Consequently, Russia became a Baltic power with open access via the sea to Europe and its market.
What was done by Peter the Great for Russia in the north (the Baltic Sea) was done later in the same century by Russian Empress (of German origin) Catherine the Great (1762−1796) in the south (the Black Sea). She was waging several successful wars from 1768 to 1792 against the Tartar Khanate in Crimea which finally led to the destruction of the Tartar state in the peninsula. It was followed by the substitution of Russian for Ottoman control along the northern littoral of the Black Sea, in the Crimean Peninsula, around the Azov Sea, and across the adjoining steppes. The seaport of Odessa was founded in 1794 and became for the region of the Black Sea of the same importance as the seaport of Archangel (est. 1584) was for the White Sea or St Petersburg for the Baltics – the focal outlet for Russian exports to Europe.
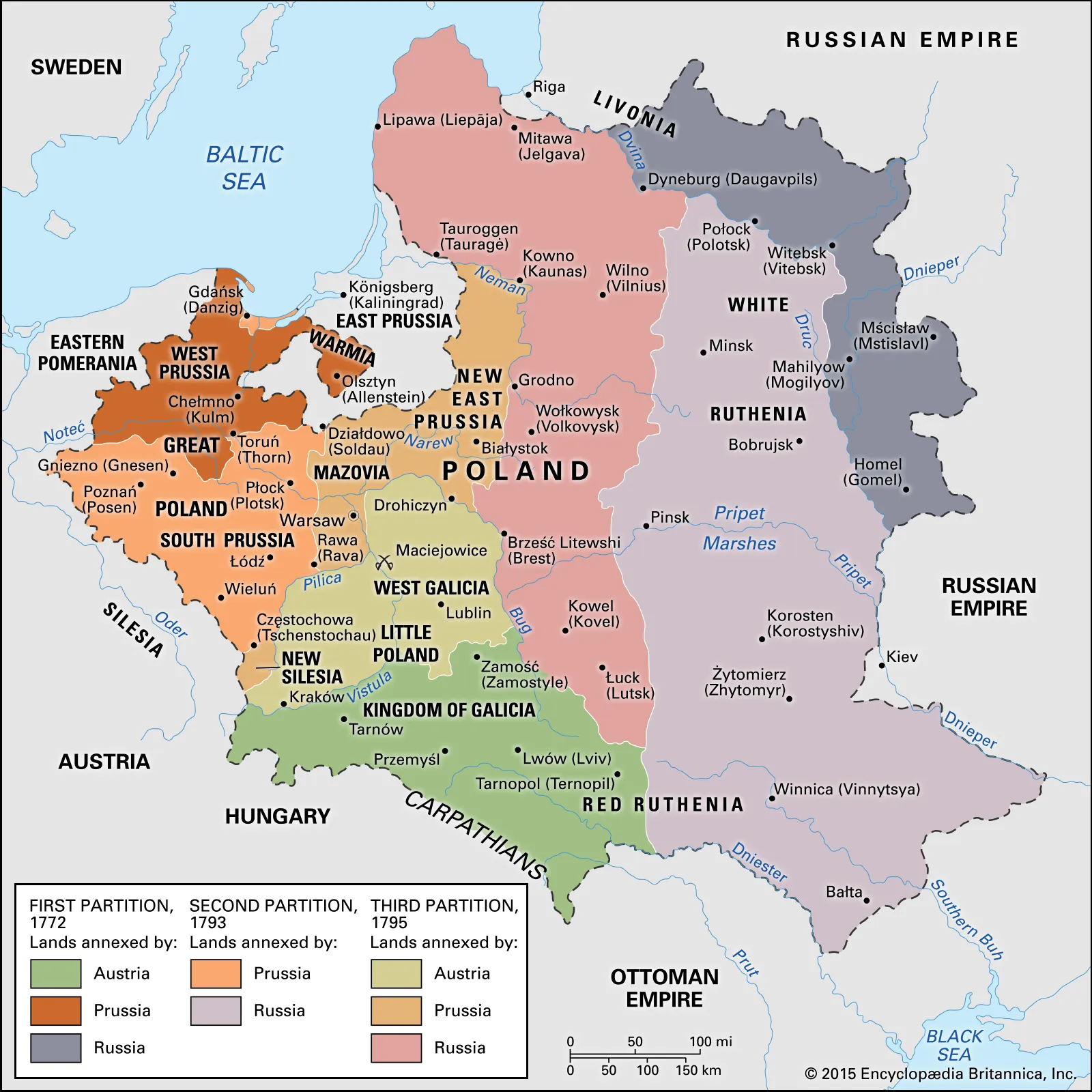
From the time of the First Partition of Poland-Lithuania (the Republic of Two Nations) in 1772 to the Vienna Congress of 1814−1815 Russia moved her state territory westward for 600 miles at the expense of Poland-Lithuania. By the three partitions of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1772, 1793, and 1795 Russian Empire gained much of the former Polish Kingdom and all Grand Duchy of Lithuania. After the collapse of Napoleon’s Grand Duchy of Warsaw, the Vienna Congress authorized Russian Emperor Alexander I (1801−1825) to become King of a reconstituted Kingdom of Poland. Russia became a leader of the Holy Alliance (Russia, Austria, and Prussia) up to the mid-19th century and, in fact, the strongest power in continental Europe with borders from Warsaw to Vladivostok. At the time of the Napoleonic Wars, Russia included the region of the South Caucasus (1806−1813).
Russia during the period from Peter the Great to the Vienna Congress experienced fast economic development, especially in the military industry. During that historical period, the Russian Empire was engaged in several wars for the purpose to obtain direct geophysical access to both the Baltic Sea in the north and the Black Sea in the south followed by pushing Russian borders westward into the territory of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth which main part of it was previously annexed from Russia and populated by Russians and other Eastern Slavs. On these East Slavonic territories incorporated into Poland-Lithuania, the Eastern Orthodox Slavs have been experiencing systematic Catholization, forced acceptance of the church union with the Vatican, and denationalization (i.e., political Russophobia). Nevertheless, these wars required a huge investment in the armaments industry and, therefore, productive metallurgical foundations. These conditions were founded by Emperor Peter the Great according to the West European pattern, fundamentally in the Urals as this region was extremely rich in iron and copper ores as well as in huge forests which have been suitable for the production of charcoal. The same Emperor founded factories, gave investment incentives, encouraged new management, and established the foundation for the further industrialization of Russia. In Central Russia, the textile and animal fat industries continued to be developed while by 1815, a new (third) industrial center arose in the north at a new capital St Petersburg.
Finally, Russia’s population in 1815 due to both territorial enlargement and prolific natural increase was significantly increased. For the year 1600, it is estimated that Russia (Moscovy) had circa 10 million inhabitants but when Peter the Great died, around 15,5 million. According to the census data in the year of the Napoleonic invasion of Russia in 1812, the Empire had already 42,75 million people (including from Europe and Asia). The population of Siberia, for instance, had grown from around 500.000 during the time of Peter the Great to some 1.400.000 when Napoleon attacked Russia. However, at that time, only 4% of the total Russia’s population was living in the urban areas, of which 30% lived in the two biggest cities – Moscow and St Petersburg.
Ex-University Professor
Research Fellow at Centre for Geostrategic Studies
Belgrade, Serbia
www.geostrategy.rs
sotirovic1967@gmail.com © Vladislav B. Sotirovic 2023
Personal disclaimer: The author writes for this publication in a private capacity which is unrepresentative of anyone or any organization except for his own personal views. Nothing written by the author should ever be conflated with the editorial views or official positions of any other media outlet or institution.
Origins of images: Facebook, Twitter, Wikimedia, Wikipedia, Flickr, Google, Imageinjection, Public Domain & Pinterest.
Read our Disclaimer/Legal Statement!
Donate to Support Us
We would like to ask you to consider a small donation to help our team keep working. We accept no advertising and rely only on you, our readers, to keep us digging the truth on history, global politics, and international relations.
FOLLOW US ON OUR SOCIAL PLATFORMS