Views: 1371
July 3, 2019 marks the 40th anniversary of when the United States’ first military assault against Afghanistan with the CIA-backed Mujahideen began. It would be a mistake to treat the present-day conflict as being separate from the U.S. intervention that began in 1979 against the then-government of the People’s Democratic Party of Afghanistan. Afghanistan was not always known as the chaotic, ‘failed state’ overrun by warlords as it is now; this phenomenon is a product of that U.S.-led regime change operation. The article below, originally published on March 30, 2019, summarizes and analyzes the events that transpired during and after the Cold War years as they relate to this often misunderstood, if not overlooked, aspect of the long war against Afghanistan.
When it comes to war-torn Afghanistan and the role played by the United States and its NATO allies, what comes first to mind for most is the ‘War on Terror’ campaign launched in 2001 by George W. Bush almost immediately after the 9/11 attacks. And understandably so, considering that the United States and its allies established a direct “boots-on-the-ground” military presence in the country that year. Not only that, but during the Bush-Cheney years, there was an aggressive propaganda campaign being played out across U.S. media outlets which used women’s rights as one of the pretexts for the continued occupation. The irony of this, however, is not lost on those who understand that the conflict in Afghanistan has a long history which, much like Syria, stretches as far back as the Cold War era — especially when it was the United States that provided support for the Mujahideen in destabilizing the country and stripping away the modernizing, progressive economic and social gains, including Afghan women’s emancipation, which the People’s Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) had fought for. With the overthrow of the independent Soviet-aligned PDPA government, the Taliban emerged as a powerful faction of the Mujahideen; the U.S. would develop a working relationship with the Taliban in 1995. The war was never truly about women’s rights or other humanitarian concerns, as Stephen Gowans explains:
“Further evidence of Washington’s supreme indifference to the rights of women abroad is evidenced by the role it played in undermining a progressive government in Afghanistan that sought to release women from the grip of traditional Islamic anti-women practices. In the 1980s, Kabul was “a cosmopolitan city. Artists and hippies flocked to the capital. Women studied agriculture, engineering and business at the city’s university. Afghan women held government jobs.” There were female members of parliament, and women drove cars, and travelled and went on dates, without needing to ask a male guardian for permission. That this is no longer true is largely due to a secret decision made in the summer of 1979 by then US president Jimmy Carter and his national security adviser Zbigniew Brzezinski to draw “the Russians into the Afghan trap” and give “to the USSR its Vietnam War” by bankrolling and organizing Islamic fundamentalist terrorists to fight a new government in Kabul led by the People’s Democratic Party of Afghanistan.
The goal of the PDPA was to liberate Afghanistan from its backwardness. In the 1970s, only 12 percent of adults were literate. Life expectancy was 42 years and infant mortality the highest in the world. Half the population suffered from TB and one-quarter from malaria.”
Moreover, and contrary to the commonly held belief that the conflict in Afghanistan started in 2001, it would be more accurate to say that the war started in 1979. As a matter of fact, the Carter Administration’s 1979 decision to overthrow the PDPA and destabilize Afghanistan is at the root of why the country is in the state that it continues to be in today.
The Cold War – a new phase in the age of imperialism
In the early 1900s, Vladimir Lenin observed that capitalism had entered into its globalist phase and that the age of imperialism had begun; this means that capitalism must expand beyond national borders, and that there is an internal logic to Empire-building and imperialist wars of aggression. Lenin defines imperialism as such:
“the concentration of production and capital has developed to such a high stage that it has created monopolies which play a decisive role in economic life; (2) the merging of bank capital with industrial capital, and the creation, on the basis of this “finance capital”, of a financial oligarchy; (3) the export of capital as distinguished from the export of commodities acquires exceptional importance; (4) the formation of international monopolist capitalist associations which share the world among themselves, and (5) the territorial division of the whole world among the biggest capitalist powers is completed. Imperialism is capitalism at that stage of development at which the dominance of monopolies and finance capital is established; in which the export of capital has acquired pronounced importance; in which the division of the world among the international trusts has begun, in which the division of all territories of the globe among the biggest capitalist powers has been completed.”
It should be clear that imperialism is not just merely the imposition of a country’s will on the rest of the world (although that is certainly a part of it). More precisely: it is a result of capital accumulation and is a process of empire-building and maintenance, which comes with holding back development worldwide and keeping the global masses impoverished; it is the international exercise of domination guided by economic interests. Thus, imperialism is less of a cultural phenomenon, and more so an economic one.
Lenin also theorized that imperialism and the cycle of World Wars were the products of competing national capitals between the advanced nations. As he wrote in Imperialism, the Highest Stage of Capitalism, World War I was about the competition between major imperialist powers — such as the competing capitals of Great Britain and Germany — over the control of and the split of plunder from colonies. Thus, finance capital was the driving force behind the exploitation and colonization of the oppressed nations; these antagonisms would eventually lead to a series of world wars as Lenin had predicted. During the First World War, the goals of the two imperial blocs of power were the acquisition, preservation, and expansion of territories considered to be strategic points and of great importance to their national economies. And during the Great Depression, protectionist measures were taken up by Britain, the United States, and France to restrict the emerging industrial nations — Germany, Italy, and Japan, also known as the Axis states — from access to more colonies and territories, thereby restricting them from access to raw materials and markets in the lead up to World War II. In particular, the two advanced capitalist industrialized powers of Germany and Japan, in their efforts to conquer new territory, threatened the economic space of Britain, the U.S., and France and threatened to take their territories, colonies, and semi-colonies by force — with Germany launching a series of aggressions in most of Europe, and Japan in Asia. WWII was, in many ways, a re-ignition of the inter-imperialist rivalry between the Anglo-French bloc and the German bloc, but with modern artillery and the significant use of aerial assaults. It was also a period of the second stage of the crisis of capitalism which saw the rise of Fascism as a reaction to Communism, with the Axis states threatening to establish a world-dominating fascist regime. For the time being, WWII would be the last we would see of world wars.
At the end of WWII, two rival global powers emerged: the United States and the Soviet Union; the Cold War was a manifestation of their ideological conflict. The Cold War era was a new phase for international capital as it saw the advent of nuclear weapons and the beginning stages of proxy warfare. It was a time when the imperialist nations, regardless of which side they were on during WWII, found a common interest in stopping the spread of Communism and seeking the destruction of the Soviet Union. By extension, these anti-communist attacks would be aimed at the Soviet-allied nations as well. This would increase the number of client states with puppet governments acting in accordance with U.S. interests who would join the NATO bloc with the ultimate aim of isolating the Soviet Union. It should also be noted that the end of WWII marked the end of competing national capitals such that now, financial capital exists globally and can move instantaneously, with Washington being the world dominating force that holds a monopoly over the global markets. Those countries who have actively resisted against the U.S. Empire and have not accepted U.S. capital into their countries are threatened with sanctions and military intervention — such as the independent sovereign nations of Syria and North Korea who are, to this day, still challenging U.S. hegemony. Afghanistan under the PDPA was one such country which stood up to U.S. imperialism and thus became a target for regime change.
In addition to implementing land reforms, women’s rights, and egalitarian and collectivist economic policies, the PDPA sought to put an end to opium poppy cultivation. The British Empire planted the first opium poppy fields in Afghanistan during the 1800s when the country was still under the feudal landholding system; up until the king was deposed in 1973, the opium trade was a lucrative business and the Afghan poppy fields produced more than 70 percent of opium needed for the world’s heroin supply. These reforms in 1978 would eventually attract opposition from the United States, which had already embarked on its anti-communist crusade, providing backing to reactionary forces dedicated to fighting against various post-colonial progressive governments, many of which were a part of the ‘Soviet Bloc’ — such as the right-wing Contras in Nicaragua who mounted violent opposition to the Sandinista government. Despite having gained independence on its own merits, Afghanistan under the PDPA — much like other Soviet-allied, postcolonial successes such as Cuba, Nicaragua, Syria, Libya, and North Korea — was seen as a “Soviet satellite” that needed to be brought back under colonial domination, and whose commodities needed to be put under the exclusive control and possession of the United States. Not only that, but it was considered a strategic point of interest that could be used to enclose upon the Soviet Union.
In order to undermine the then-newly formed and popular PDPA government, the Carter administration and the CIA began the imperialist intervention by providing training, financial support, and weapons to Sunni extremists (the Mujahideen) who started committing acts of terrorism against schools and teachers in rural areas. With the assistance of the Saudi and Pakistani militaries, the CIA gathered together ousted feudal landlords, reactionary tribal chiefs, sectarian Sunni clerics, and cartel drug lords to form a coalition to destabilize Afghanistan. On September 1979, Noor Mohammed Taraki — the first PDPA leader and President of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan — was assassinated during the events of the CIA-backed coup, which was quickly stopped by the Afghan army. However, by late 1979, the PDPA was becoming overwhelmed by the large-scale military intervention by U.S. proxy forces — a combination of foreign mercenaries and Afghan Ancien Régime-sympathizers — and so they decided to make a request to the USSR to deploy a contingent of troops for assistance. The Soviet intervention provided some much-needed relief for the PDPA forces — if only for the next ten years, for the U.S. and Saudi Arabia “upped the ante” by pouring about $40 billion into the war and recruiting and arming around 100,000 more foreign mercenaries. In 1989, Mikhail Gorbachev would call on the Soviet troops to be withdrawn, and the PDPA was eventually defeated with the fall of Kabul in April 1992. Chaos ensued as the Mujahideen fell into infighting with the formation of rival factions competing for territorial space and also wreaking havoc across cities, looting, terrorizing civilians, hosting mass executions in football stadiums, ethnically-cleansing non-Pashtun minorities, and committing mass rapes against Afghan women and girls. Soon afterwards in 1995, one of the warring factions, the Taliban, consolidated power with backing from the United States, Saudi Arabia, and Pakistan. On September 28, 1996 the last PDPA Presidential leader, Mohammad Najibullah, was abducted from his local UN compound (where he had been granted sanctuary), tortured, and brutally murdered by Taliban soldiers; they strung his mutilated body from a light pole for public display.
A renewed opium trade, and the economic roots of Empire-building
“Once the heroin left these labs in Pakistan’s northwest frontier, the Sicilian Mafia imported the drugs into the U.S., where they soon captured sixty percent of the U.S. heroin market. That is to say, sixty percent of the U.S. heroin supply came indirectly from a CIA operation. During the decade of this operation, the 1980s, the substantial DEA contingent in Islamabad made no arrests and participated in no seizures, allowing the syndicates a de facto free hand to export heroin.”
It is apparent that by putting an end to the cultivation of opium poppy, in addition to using the country’s resources to modernize and uplift its own population, the independent nationalist government of the PDPA was seen as a threat to U.S. interests that needed to be eliminated. A major objective of the U.S.-led Mujahideen — or any kind of U.S. military-led action for that matter — against Afghanistan had always been to restore and secure the opium trade. After all, it was during the 1970s that drug trafficking served as the CIA’s primary source of funding for paramilitary forces against anti-imperialist governments and liberation movements in the Global South, in addition to protecting U.S. assets abroad. Also, the CIA’s international drug trafficking ties go as far back as 1949, which is the year when Washington’s long war on the Korean Peninsula began. The move by the PDPA to eradicate opium-poppy harvesting and put an end to the exploitation brought about by the drug cartels was seen as “going too far” by U.S. imperialists. A significantly large loss in opium production would mean a huge loss in profits for Wall Street and major international banks, which have a vested interest in the drug trade. In fact, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) reported that money-laundering made up 2-5% of the world economy’s GDP and that a large percentage of the annual money-laundering, which was worth 590 billion to 1.5 trillion dollars, had direct links to the drug trade. The profits generated from the drug trade are often placed in American-British-controlled offshore banks.
The rationale behind the PDPA’s campaign to eradicate the opium poppy harvest was based not only on practical health reasons, but also on the role played by narcotics in the history of colonialism in Asia. Historically, cartel drug lords enabled imperialist nations, served bourgeois interests, and used cheap exploited slave labour. Oftentimes, the peasants who toiled in these poppy fields would find themselves becoming addicted to heroin in addition to being, quite literally, worked to death. Cartels are understood to be monopolistic alliances in which partners agree on the conditions of sale and terms of payment and divide the markets amongst themselves by fixing the prices and the quantity of goods to be produced. Now, concerning the role of cartels in ‘late-stage capitalism’, Lenin wrote:
“Monopolist capitalist associations, cartels, syndicates and trusts first divided the home market among themselves and obtained more or less complete possession of the industry of their own country. But under capitalism the home market is inevitably bound up with the foreign market. Capitalism long ago created a world market. As the export of capital increased, and as the foreign and colonial connections and “spheres of influence” of the big monopolist associations expanded in all ways, things “naturally” gravitated towards an international agreement among these associations, and towards the formation of international cartels.
This is a new stage of world concentration of capital and production, incomparably higher than the preceding stages.”
International cartels, especially drug cartels, are symptoms of how capital has expanded globally and has adapted to create a global wealth divide based on the territorial division of the world, the scramble for colonies, and “the struggle for spheres of influence.” More specifically, international cartels serve as stewards for the imperialist nations in the plundering of the oppressed or colonized nations. Hence the mass campaigns to help end addictions and to crack down on drug traffickers which were not only implemented in Afghanistan under the PDPA, but in Revolutionary China in 1949 and by other anti-imperialist movements as well. Of course, the opium traffickers and their organized crime associates in Afghanistan saw the campaign against opium poppy cultivation, among other progressive reforms, as an affront; this made them ideal recruits for the Mujahideen.
But why the “breakdown” in the relationship between the U.S. and the Taliban from the early 2000s and onwards? Keep in mind that, again, the members of the Taliban were amongst the various factions that made up the Mujahideen whose partnership with the United States extends as far back as the late 1970s; and it was clear that the U.S. was aware that it was working with Islamic fundamentalists. The human rights abuses committed by the Taliban while in power were well-documented before their relations with the U.S. soured by the year 2000. What made these relations turn sour was the fact that the Taliban had decided to drastically reduce the opium poppy cultivation. This led to the direct U.S. military intervention of 2001 in Afghanistan and the subsequent overthrow of the Taliban; the U.S. used the attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon as a pretext even if there was no proof that the Taliban had a hand in them or had been in contact with Osama bin Laden at all during that time. The U.S. would soon replace the Taliban with another faction of the Mujahideen that was more compliant with the rules that the imperialists had set out. In other words, the Taliban were ousted not necessarily because they posed a significant challenge to U.S. hegemony as the PDPA had, or because of their treatment of women — nor were they hiding Osama bin Laden; it was because they had become more of liabilities than assets. It is yet another case of the Empire discarding its puppets when they have outlived their usefulness due to incompetence and being unable to “follow the rules properly” — not unlike the U.S. removal of military dictator Manuel Noriega who was staunchly pro-American and who, in collaboration with fellow CIA asset and notorious cartel drug kingpin Pablo Escobar, previously sold drugs for the CIA to help finance the anti-communist campaign in Central America.
Although the United States has always been one of the top producers of oil in the world, another reason for establishing a permanent U.S. military presence in Afghanistan was to gain control over its vast untapped oil reserves, which the U.S. had known about prior to 9/11. Oil is yet another lucrative commodity, and ensuring that Afghanistan had a compliant government that would acquiesce to its demands was important for the U.S. in this aspect as well. Naturally, the nationalist government of the PDPA was also seen as a threat to the profit-making interests of U.S. oil companies, and any nation that was an independent oil producer (or merely a potential independent oil producer, in Afghanistan’s case) was seen as an annoying competitor by the United States. However, Afghanistan would not begin its first commercial oil production until 2013, partly because of the ongoing geopolitical instability, but also because opium production continues to dominate the economy. Plus, it is likely that neither the monarchy nor the PDPA realized that there existed such vast untapped oil reserves since there were very limited volumes of oil (compared to the higher volumes of natural gas) being produced from 1957 to 1989, and which stopped as soon as the Soviet troops left. Later, reassessments were made during the 1990s; hence the U.S. ‘discovery’ of the untapped petroleum potential. But, when intensive negotiations between U.S.-based oil company Unocal and the Taliban went unresolved in 1998 due to a dispute over a pipeline deal that the latter wanted to strike with a competing Argentine company, it would lead to growing tensions between the U.S. and the Taliban. The reason for the dispute was that Unocal wanted to have primary control over the pipeline located between Afghanistan and Pakistan that crossed into the Indian Ocean. From this point on, the U.S. was starting to see the Taliban as a liability in its prerogative of establishing political and economic dominance over Central and West Asia.
In either case, oil and other “strategic” raw materials such as opium are essential for the U.S. to maintain its global monopolistic power. It is here that we see a manifestation of the economic roots of empire-building.
The original “moderate rebel”
One of the key players in the anti-Soviet, U.S.-led regime change project against Afghanistan was Osama bin Laden, a Saudi-born millionaire who came from a wealthy, powerful family that owns a Saudi construction company and has had close ties to the Saudi royal family. Before becoming known as America’s “boogeyman”, Osama bin Laden was put in charge of fundraising for the Mujahideen insurgents, creating numerous charities and foundations in the process and working in coordination with Saudi intelligence (who acted as liaisons between the fighters and the CIA). Journalist Robert Fisk even gave bin Laden a glowing review, calling him a “peace warrior” and a philanthropist in a 1993 report for the Independent. Bin Laden also provided recruitment for the Mujahideen and is believed to have also received security training from the CIA. And in 1989, the same year that Soviet troops withdrew, he founded the terrorist organization Al Qaeda with a number of fighters he had recruited to the Mujahideen. Although the PDPA had already been overthrown, and the Soviet Union was dissolved, he still maintained his relationship with the CIA and NATO, working with them from the mid-to-late 1990s to provide support for the secessionist Bosnian paramilitaries and the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA) in the destruction and dismantling of Yugoslavia.
The United States would eventually turn Bin Laden into a scapegoat after the 2001 terrorist attacks, while still maintaining ties to his family and providing arms, training, and funding to Al Qaeda and its affiliates (rebranded as “moderate rebels” by the Western media) in its more recent regime change project against Syria, which started in 2011. The Mujahideen not only gave birth to Al Qaeda, but it would set a precedent for the United States’ regime-change operations in later years against the anti-imperialist governments of Libya and Syria.
Furthermore, proxy warfare enables control of public opinion, thus allowing the U.S. government to escape public scrutiny and questions about legal authorization for war. With opposition from the general public essentially under control, consent for U.S.-led wars does not need to be obtained, especially when the U.S. military is running them from “behind the scenes” and its involvement looks less obvious. Indeed, the protests against the war on Vietnam in the United States and other Western countries saw mass turnouts.
And while the U.S.-led aggression in Vietnam did involve proxy warfare to a lesser degree, it was still mostly fought with American “boots-on-the-ground”, much like the 2001 renewed U.S.-led aggression against Afghanistan and the 2003 invasion of Iraq. In contrast, the U.S. assault on Afghanistan that began in 1979 saw little to no protest. The Mujahideen even garnered support from large portions of the Western left who joined the chorus of voices in the Western mainstream media in demonizing the PDPA — a relentless imperialist propaganda campaign that would be repeated in later years during the U.S. wars on Libya and Syria, with the difference being that social media had not yet gained prominence at the time of the initial assault on Afghanistan. This leads to the next question: why recruit some of the most reactionary social forces abroad, many of whom represent complete backwardness?
In Afghanistan, such forces proved useful in the mission to topple the modernizing government of the PDPA, especially when their anti-modernity aspirations intersected with U.S. foreign policy; these ultra-conservative forces continue to be deployed by the United States today. In fact, the long war on Afghanistan shares many striking similarities with the long war on Syria, with the common theme of U.S. imperialism collaborating with violent Sunni extremists to topple the secular, nationalist and anti-imperialist governments of these two former ‘Soviet bloc’ countries. And much like the PDPA, the current and long-time government of the Ba’ath Arab Socialist Party in Syria has made many strides towards achieving national liberation and economic development, which have included: taking land from aristocratic families (a majority of whom were Sunni Muslims while Shia Muslims, but especially Alawites, traditionally belonged to the lower classes and were treated as second class citizens in pre-Ba’athist Syria) and redistributing and nationalizing it, making use of Syria’s oil and gas reserves to modernize the country and benefit its population, and upholding women’s rights as an important part of the Ba’athist pillars.
Some of these aristocratic landlords, just like their Afghan counterparts, would react violently and join the Muslim Brotherhood who, with CIA-backing, carried out acts of terrorism and other atrocities in Hama as they made a failed attempt to topple the government of Hafez al Assad in 1982.
The connection between the two is further solidified by the fact that it was the Mujahideen from which Al Qaeda emerged; both are inspired by Wahhabist ideology, and one of their chief financiers is the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (as well as Israel, a regional imperial power and a key ally of the United States). In either case, these Wahhabi-inspired forces were vehemently opposed to modernization and development, and would much rather keep large sections of the population impoverished, as they sought to replace the PDPA and the Ba’athists with Sunni fundamentalist, anti-Shia, theological autocracies — Saudi-style regimes, in other words.
These reactionary forces are useful tools in the CIA’s anti-communist projects and destabilization campaigns against independent nationalist governments, considering that the groups’ anti-modernity stance is a motivating factor in their efforts to sabotage economic development, which is conducive to ensuring a favourable climate for U.S. capital interests. It also helps that these groups already saw the nationalist governments of the PDPA and the Syrian Ba’ath party as their ‘archenemy’, and would thus fight them to the death and resort to acts of terrorism against the respective civilian populations.
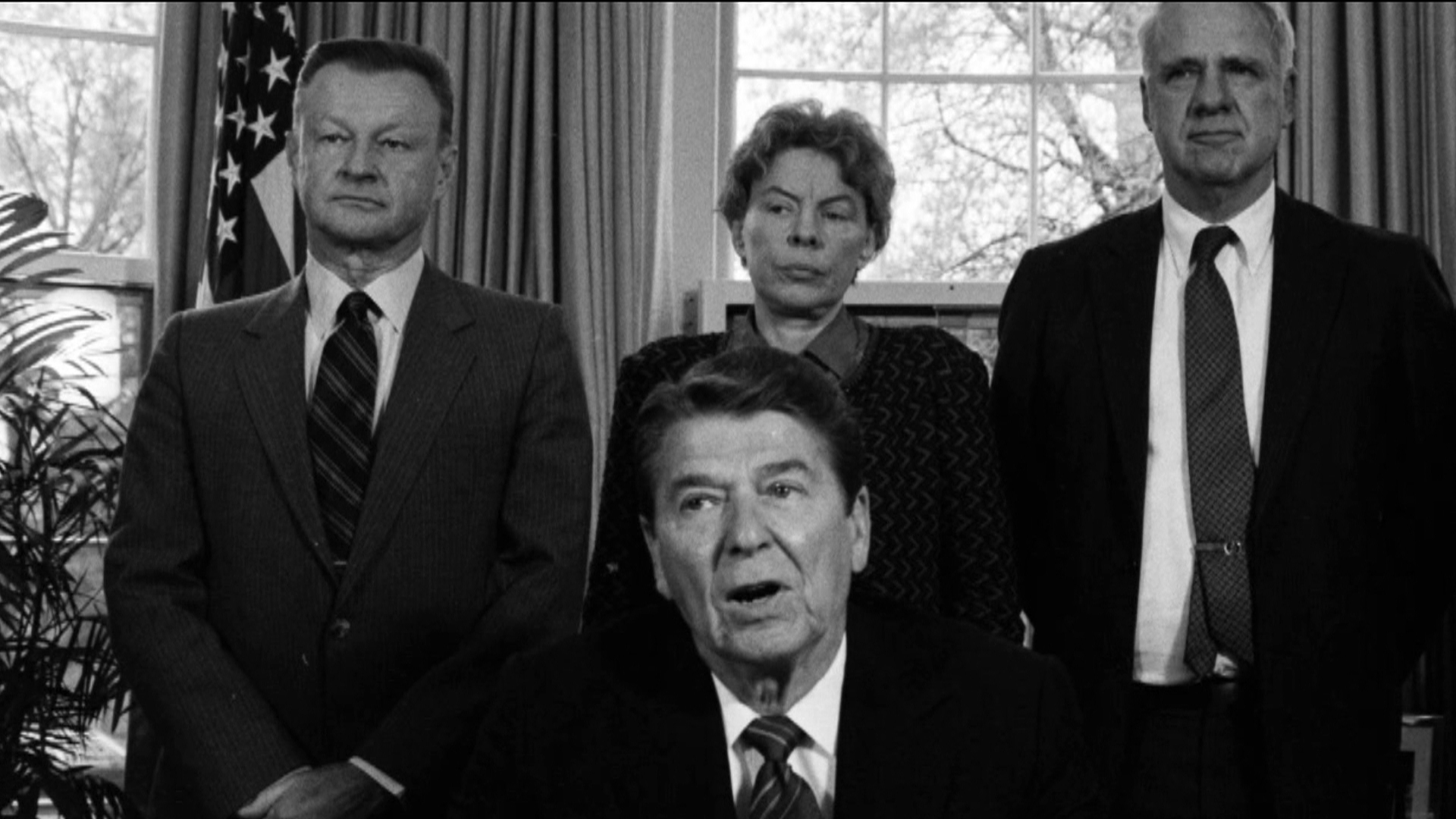
Zbigniew Brzezinski stated in a 1998 interview with Le Nouvel Observateur in response to the following question:
Q: And neither do you regret having supported the Islamic fundamentalism, having given arms and advice to future terrorists?
[Brzezinski]: What is most important to the history of the world? The Taliban or the collapse of the Soviet empire? Some stirred-up Moslems or the liberation of Central Europe and the end of the cold war?
Once again, he makes it clear that the religious extremism of the Mujahideen fighters was not an issue for Washington because the real political value lay in eliminating the PDPA and putting an end to Soviet influence in the Greater Middle East, which would give the U.S. the opportunity to easily access and steal the country’s wealth. And in order to justify the U.S. imperialist intervention in Afghanistan, as well as to obscure the true nature of the Mujahideen fighters, the intervention needed to be accompanied by a rigorous mass media campaign. The Reagan administration — knowing full well that American mainstream media has international influence — continued the war that the Carter administration started and saw it as an opportunity to “step up” its domestic propaganda war, considering that the American general public was still largely critical of the Vietnam War at the time.
As part of the aggressive imperialist propaganda campaign, anyone who dared to publicly criticize the Mujahideen was subjected to character assassination and was pejoratively labelled a “Stalinist” or a “Soviet apologist”, which are akin to labels such as “Russian agent” or “Assadist” being used as insults today against those who speak out against the U.S.-backed terrorism in Syria. There were also careful rebranding strategies made specifically for Osama bin Laden and the Mujahideen mercenaries, who were hailed as “revolutionary freedom fighters” and given a romantic, exoticized “holy warrior” makeover in Western media; hence the title of this section. The Mujahideen mercenaries were even given a dedication title card at the end of the Hollywood movie Rambo III which read, “This film is dedicated to the brave Mujahideen fighters of Afghanistan”; the film itself added to the constructed romantic image as it portrayed the Mujahideen fighters as heroes, while the Soviet Union and the PDPA were portrayed as the cartoonish villains. The Rambo film franchise is well known for its depiction of the Vietnamese as “savages” and as the aggressors in the U.S. war on Vietnam, which is a blatant reversal of the truth.
The Hollywood blockbuster franchise would be used to make the Mujahideen more palatable to Western audiences, as this unabashed, blatantly anti-Soviet propaganda for U.S. imperialism attracted millions of viewers with one of the largest movie marketing campaigns of the time. Although formulaic, the films are easily consumable because they appeal to emotion and, as Michael Parenti states in Dirty Truths, “The entertainment industry does not merely give the people what they want: it is busy shaping those wants,” (p. 111). Rambo III may not have been critically acclaimed, but it was still the second most commercially successful film in the Rambo series, grossing a total of $189,015,611 at the box office. Producing war propaganda films is nothing new and has been a long staple of the Hollywood industry, which serves capitalist and imperialist interests. But, since the blockbuster movie is one of the most widely available and distributed forms of media, repackaging the Mujahideen into a popular film franchise was easily one of the best ways (albeit cynical) to justify the war, maintaining the American constructed narrative and reinforcing the demonization campaign against Soviet Russia and the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan. Now, outside of the cinema, CBS News went as far as to air fake battle footage meant to help perpetuate the myth that the Mujahideen mercenaries were “freedom fighters”; American journalists Paul Fitzgerald and Elizabeth Gould, although decidedly biased against the Soviet Union and its allies, documented this ruse in which the news channel participated. In terms of proxy warfare, these were just some of the ways used to distract from the fact that it was a U.S.-led war.
In Afghanistan, proxy forces provided a convenient cover because they drew attention away from the fact that U.S. imperialism was the root cause of the conflict. The insurgents also helped to demonize the targets of U.S. foreign policy, the PDPA and the Soviet Union, all the while doing the majority of the physical combat in place of the American military. In general, drawing attention away from the fact that it has been the United States “pulling the strings” all along, using proxy forces helps Washington to maintain plausible deniability in regard to its relationship with such groups. If any one of these insurgents becomes a liability, as what had happened with the Taliban, they can just as easily be disposed of and replaced by more competent patsies, while U.S. foreign policy goes unquestioned. Criminal gangs and paramilitary forces are thus ideal and convenient tools for U.S. foreign policy. With the rule of warlords and the instability (namely damage to infrastructure, de-industrialization, and societal collapse) that followed after the toppling of the PDPA, Afghanistan’s standard of living dropped rapidly, leading to forced mass migrations and making the country all the more vulnerable to a more direct U.S. military intervention — which eventually did happen in 2001.
Zbigniew Brzezinski: godfather of colour revolutions and proxy wars, architect of the Mujahideen
The late Brzezinski was a key figure in U.S. foreign policy and a highly influential figure in the Council on Foreign Relations. Although the Polish-American diplomat and political scientist was no longer the National Security Advisor under Ronald Reagan’s presidency, he still continued to play a prominent role in enforcing U.S. foreign policy goals in upholding Washington’s global monopoly. The liberal Cold War ideologue’s signature strategy consisted of using the CIA to destabilize and force regime-change onto countries whose governments actively resisted against Washington. Such is the legacy of Brzezinski, whose strategy of funding the most reactionary anti-government forces to foment chaos and instability while promoting them as “freedom fighters” is now a longstanding staple of U.S. imperialism.
How were the aggressive propaganda campaigns which promoted the Mujahideen mercenaries as “freedom fighters” able to garner support for the aggression against the former Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from so many on the Western left who had previously opposed the war on Vietnam? It was the through the CIA’s use of ‘soft-power’ schemes, because leftist opinion also needed to be controlled and manipulated in the process of carrying out U.S. foreign and public policy. Brzezinski mastered the art of targeting intelligentsia and impressionable young people in order to make them supportive of U.S. foreign policy, misleading a significant number of people into supporting U.S.-led wars.
The CIA invested money into programs that used university campus, anti-Soviet “radical leftist activists” and academics (as well as artists and writers) to help spread imperialist propaganda dressed up in vaguely “leftist”-sounding language and given a more “hip”, “humanitarian”, “social justice”, “free thinker” appeal. Western, but especially American, academia has since continued to teach the post-modernist “oppression theory” or “privilege theory” to students, which is anti-Marxist and anti-scientific at its core. More importantly, this post-modernist infiltration was meant to distract from class struggle, to help divert any form of solidarity away from anti-imperialist struggles, and to foster virulent animosity towards the Soviet Union among students and anyone with ‘leftist’ leanings. Hence the phenomenon of identity politics that continues to plague the Western left today, whose strength was effectively neutered by the 1970s. Not only that, but as Gowans mentions in his book, Patriots, Traitors and Empires: The Story of Korea’s Struggle for Freedom:
“U.S. universities recruit talented individuals from abroad, instill in them the U.S. imperialist ideology and values, and equip them with academic credentials which conduce to their landing important political positions at home. In this way, U.S. imperial goals indirectly structure the political decision-making of other countries.” (pp. 52-53)
And so we have agencies and think-tanks such as the National Endowment for Democracy (NED) which has scholarly appeal and actively interferes in elections abroad — namely, in countries that are targets of U.S. foreign policy. Founded in 1983 by Reagan and directed by the CIA, the agency also assists in mobilizing coups and paid “dissidents” in U.S.-led regime change projects, such as the 2002 failed attempt against Hugo Chavez in Venezuela, as well as helping to create aggressive media campaigns that demonize targeted nations. Another instance of this “soft power” tactic of mobilizing U.S.-backed “dissidents” in targeted nations are the number of Sunni Islamic fundamentalist madrassas (schools) sponsored by the CIA and set up by Wahhabi missionaries from Saudi Arabia in Afghanistan — which started to appear in increasing numbers during the 1980s, reaching over 39,000 during the decade. Afghanistan’s public education institutions were largely secular prior to the fall of Kabul in 1992; these madrassas were the direct, ideological and intellectual antitheses to the existing institutions of education. The madrassas acted as centres for cult-like brainwashing and were essentially CIA covert psychological operations (psy-ops) intended to inspire divisiveness and demobilize younger generations of Afghans in the face of imperial onslaught so that they would not unite with the wider PDPA-led nationalist resistance to imperialism.
The NED’s founding members were comprised of Cold War ideologues which included Brzezinski himself, as well as Trotskyists who provided an endless supply of slurs against the Soviet Union. It was chiefly under this agency, and with direction provided by Brzezinski, that America produced artists, “activists”, academics, and writers who presented themselves as “radical leftists” and slandered the Soviet Union and countries that were aligned with it — which was all part of the process of toppling them and subjugating them to U.S. free market fundamentalism. With Brzezinski having mastered the art of encouraging postmodernism and identity politics among the Western left in order to weaken it, the United States not only had military and economic might on its side but also highly sophisticated ideological instruments to help give it the upper hand in propaganda wars.
These “soft power” schemes are highly effective in masking the brutality of U.S. imperialism, as well as concealing the exploitation of impoverished nations. Marketing the Mujahideen mercenaries as “peace warriors” while demonizing the PDPA and referring to the Soviet assistance as an “invasion” or “aggression” marked the beginning of the regular use of “humanitarian” pretexts for imperialist interventions. The Cold War era onslaught against Afghanistan can thus be seen as the template for the NATO-led regime change projects against Yugoslavia, Libya, and Syria, which not only involved the use of U.S.-backed proxy forces but also “humanitarian” pretexts being presented in the aggressive propaganda campaigns against the targeted countries. It was not until 2002, however, that then-American UN representative Samantha Powers, as well as several U.S.-allied representatives, would push the United Nations to officially adopt the “Responsibility to Protect” (R2P) doctrine into the Charter — which was in direct contradiction to the law that recognizes the violation of a nation’s sovereignty as a crime. The R2P doctrine was born out of the illegal 78-day NATO air-bombing of Yugoslavia from March 24 to June 10, 1999. And although plans to dismantle Yugoslavia go as far back as 1984, it was not until much of the 1990s that NATO would begin openly intervening — with more naked aggression — starting with the funding and support for secessionist paramilitary forces in Bosnia between 1994-1995. It then sealed the 1999 destruction of Yugoslavia with with the balkanization of the Serbian province of Kosovo. In addition to the use of terrorist and paramilitary groups as proxy forces which received CIA-training and funding, another key feature of this “humanitarian” intervention was the ongoing demonization campaigns against the Serbs, who were at the centre of a vicious Western media propaganda war. Some of the most egregious parts of these demonization campaigns — which were tantamount to slander and libel — were the claims that the Serbs were “committing genocide” against ethnic Albanians. The NATO bombing campaign was illegal since it was given no UN Security Council approval or support.
Once again, Brzezinski was not the National Security Advisor during the U.S.-led campaign against Yugoslavia. However, he still continued to wield influence as a member of the Council on Foreign Relations, a private organization and Wall Street think tank. The Council on Foreign Relations is intertwined with highly influential NGOs who are essentially propaganda mouthpieces for U.S. foreign policy, such as Human Rights Watch, which has fabricated stories of atrocities allegedly committed by countries targeted by U.S. imperialism. Clearly, unmitigated U.S. imperial aggression did not end with the destruction of the former Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, nor with the dissolution of the Soviet Union. The post-Cold War years were a continuation of U.S. imperialism’s scramble for more spheres of influence and global domination; it was also a scramble for what was left of the former ‘Soviet bloc’ and Warsaw Pact. The dismantling of Yugoslavia was, figuratively speaking, the ‘final nail in the coffin’ of whatever ‘Soviet influence’ was left in Eastern Europe.
The demise of the Soviet Union and the “Afghan trap” question
The sabotage and subsequent dissolution of the Soviet Union meant that only one global hegemon remained, and that was the United States. Up until 1989, the Soviet Union had been the barrier that was keeping the United States from launching a more robust military intervention in Afghanistan, as well as in Central and West Asia. While pulling out did not immediately cause the defeat of Kabul as the PDPA government forces continued to struggle for another three years, Mikhail Gorbachev’s decision to withdraw Soviet troops arguably had a detrimental impact on Afghanistan for many years to come. Although there was no Soviet military assistance in the last three years of Najibullah’s presidency, Afghanistan continued to receive aid from the USSR, and some Soviet military advisers (however limited in their capacity) still remained; despite the extreme difficulties, and combined with the nation’s still-relatively high morale, this did at least help to keep the government from being overthrown immediately. This defied U.S. expectations as the CIA and the George H.W. Bush administration had believed that the government of Najibullah would fall as soon as Soviet troops were withdrawn. But what really hurt the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan’s army was when the Soviet Union was dismantled in 1991; almost as soon as the dissolution happened and Boris Yeltsin (with U.S. backing) took over as Russia’s president, the aid stopped coming and the government forces became unable to hold out for much longer. The U.S. aggression was left unchecked, and to this day Afghanistan has not seen geopolitical stability and has since been a largely impoverished ‘failed state’, serving as a training ground for terrorist groups such as ISIS and Al Qaeda. It continues to be an anarchic battleground between rival warlords which include the ousted Taliban and the U.S. puppet government that replaced them.
But, as was already mentioned above, the “Afghan trap” did not, in and of itself, cause the dismantling of the Soviet Union. In that same interview with Le Nouvel Observateur, Brzezinski had this to say in response to the question about setting the “trap”:
Q: Despite this risk, you were an advocate of this covert action. But perhaps you yourself desired this Soviet entry into war and looked to provoke it?
[Brzezinski]: It isn’t quite that. We didn’t push the Russians to intervene, but we knowingly increased the probability that they would.
Likewise with Cuba and Syria, the USSR had a well-established alliance with the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, one of mutual aid and partnership. Answering Kabul’s explicit request for assistance was a deliberate and conscious choice made by Moscow, and it just so happened that the majority of Afghans welcomed it. For any errors that Leonid Brezhnev, the General Secretary at the time, may have made (which do deserve a fair amount of criticism, but are not the focus of this article), the 1979 decision to intervene on behalf of Afghanistan against U.S. imperialism was not one of them. It is true that both the Soviet and the U.S. interventions were military interventions, but the key difference is that the U.S. was backing reactionary forces for the purposes of establishing colonial domination and was in clear violation of Afghan sovereignty. Consider, too, that Afghanistan had only deposed of its king in 1973, just six years before the conflict began. The country may have moved quickly to industrialize and modernize, but it wasn’t much time to fully develop its military defenses by 1979.
Image below: Mikhail Gorbachev accepts the Nobel Peace Prize from George H.W. Bush on October 15, 1990. Many Russians saw this gesture as a betrayal, while the West celebrated it, because he was being awarded for his capitulation to U.S. imperialism in foreign and economic policy.
Other than that, perhaps it would be more accurate to say that the Soviet Union imploded due to an accumulating number of factors: namely, the gradual steps that U.S. foreign policy had taken over the years to cripple the Soviet economy, especially after the deaths of Brezhnev and Yuri Andropov. How Gorbachev responded during the U.S.-led onslaught against Afghanistan certainly helped to exacerbate the conditions that led to the dissolution. After the deaths of Brezhnev and Andropov, the Soviet Union’s economy became disorganized and was being liberalized during much of the 1980s. Not only that, but the Reagan administration escalated the arms race, which intensified after they had scrapped the ‘detente’ that was previously made in the mid-1970s. Even prior to Reagan’s hardline, bombastic rhetoric and escalation against the USSR, the Soviet Union was already beginning to show signs of strain from the arms race during the late-1970s. However, in spite of the economic strains, during the height of the war the organized joint operations between the Soviet army and the Afghan army saw a significant amount of success in pushing back against the Mujahideen with many of the jihadist leaders either being killed or fleeing to Pakistan. Therefore, it is erroneous to say that intervening in Afghanistan on behalf of the Afghan people “did the Soviet Union in.”
In a misguided and ultimately failed attempt to spur economic growth rates, Gorbachev moved to end the Cold War by withdrawing military support from allies and pledging cooperation with the United States who promised “peace”. When he embraced Neoliberalism and allowed for the USSR to be opened to the U.S.-dominated world capitalist economy, the Soviet economy imploded and the effects were felt by its allies. It was a capitulation to U.S. imperialism, in other words; and it led to disastrous results not only in Afghanistan, but in several other countries as well. These include: the destruction of Yugoslavia, both wars on Iraq, and the 2011 NATO invasion of Libya. Also, Warsaw Pact members in Eastern Europe were no longer able to effectively fight back against U.S.-backed colour revolutions; some of them would eventually be absorbed as NATO members, such as Czechoslovakia which was dissolved and divided into two states: the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Without Soviet Russia to keep it in check, the United States was able to launch an unrestrained series of aggressions for nearly two decades. Because of his decision to withdraw from the arms race altogether, in a vain attempt to transform the Soviet Union into a social democracy akin to those of the Nordic countries, Gorbachev had deprived the Russian army of combat effectiveness by making significant cuts to its defense budget, which is partly why they were forced to evacuate. Not only that, but these diplomatic and military concessions with the United States gave them no benefit in return, hence the economic crisis in Russia during the Yeltsin years. Suffice to say, the Gorbachev-Yeltsin years are not remembered fondly in Russia and many regard Gorbachev as a traitor and Western agent who helped to bring the Soviet Union to its collapse. In more recent years, efforts are being made to assess the actions taken by Gorbachev with regards to Afghanistan; this includes going against and revising the resolution put forth by him which suggested that the USSR intervention was “shameful”.
In short, Afghanistan did not cause the Soviet Union’s demise even if it required large military spending. More accurately: it was Gorbachev’s impulsive decision to quickly discard the planned economy in favour of a market economy in order to appease the United States, who made the false promise that NATO would not expand eastward. If there was a real “trap”, it was this and Gorbachev played right into the hands of U.S. imperialism; and so, the Soviet Union received its devastating blow from the United States in the end — not from a small, minor nation such as Afghanistan which continues to suffer the most from the effects of these past events. For many years, but especially since the end of WWII, the United States made ceaseless efforts to undermine the USSR, adding stress upon stress onto its economy, in addition to the psychological warfare waged through the anti-Soviet propaganda and military threats against it and its allies. Despite any advances made in the past, the Soviet Union’s economy was still not as large as that of the United States. And so, in order to keep pace with NATO, the Soviet Union did not have much of a choice but to spend a large percentage of its GDP on its military and on helping to defend its allies, which included national liberation movements in the Third World, because of the very real and significant threat that U.S. imperialism posed. If it had not spent any money militarily, its demise would most likely have happened much sooner. But eventually, these mounting efforts by U.S. imperialism created a circumstance where its leadership under Gorbachev made a lapse in judgment, reacting impulsively and carelessly rather than acting with resilience in spite of the onslaught.
It should also be taken into account that WWII had a profound impact on Soviet leadership — from Joseph Stalin to Gorbachev — because even though the Red Army was victorious in defeating the Nazis, the widespread destruction had still placed the Soviet economy under an incredible amount of stress and it needed time to recover. Meanwhile, the convenient geographical location of the United States kept it from suffering the same casualties and infrastructural damage seen across Europe and Asia as a result of the Second World War, which enabled its economy to recover much faster and gave it enough time to eventually develop the U.S. Dollar as the international currency and assert dominance over the world economy. Plus, the U.S. had accumulated two-thirds of the world’s gold reserves by 1944 to help back the Dollar; and even if it lost a large amount of the gold, it would still be able to maintain Dollar supremacy by developing the fiat system to back the currency. Because of the destruction seen during WWII, it is understandable that the Soviet Union wanted to avoid another world war, which is why it also made several attempts at achieving some kind of diplomacy with the United States (before Gorbachev outright capitulated). At the same time, it also understood that maintaining its military defenses was important because of the threat of a nuclear war from the United States, which would be much more catastrophic than the Nazis’ military assaults against the Soviet Union since Hitler did not have a nuclear arsenal. This was part of a feat that U.S. imperialism was able to accomplish that ultimately overshadowed British, French, German, and Japanese imperialism, which Brzezinski reveals in his book, The Grand Chessboard: American Primacy and its Geostrategic Imperatives: an unparalleled military establishment that, by far, had the most effective global reach which allowed the U.S. to “project forces over long distances”, helping it to assert its global domination and impose its “political will”. And what makes the American Empire distinct from the Japanese Empire, British Empire, and other European empires is that one of the bases for its ideology is the socially constructed international hierarchy of nations, and not races as was the case with the other aforementioned empires. This constructed international hierarchy of nations is more effective because it means not only greater expansionism, but also the greater ability to exercise global primacy and supremacy. More specific to Central Asia and the Middle East, the Wahhabist and Salafist groups propped up by the CIA were always intended to nurture sectarianism and discord in order to counter a mass, broad-based united front of nations against imperialism — an example of divide-and-conquer, which is an age-old tradition of empire, except this time with Neoliberal characteristics.
Cold War 2.0? American Supremacy marches on
The present-day anti-Russia hysteria is reminiscent of the anti-Soviet propaganda of the Cold War era; while anti-communism is not the central theme today, one thing remains the same: the fact that the U.S. Empire is (once again) facing a formidable challenge to its position in the world. After the Yeltsin years were over, and under Vladimir Putin, Russia’s economy eventually recovered and moved towards a more dirigiste economy; and on top of that, it moved away from the NATO fold, which triggered the old antagonistic relationship with the United States. Russia has also decided to follow the global trend of taking the step towards reducing reliance on the U.S. dollar, which is no doubt a source of annoyance to the U.S. capitalist class. It seems that a third world war in the near future is becoming more likely as the U.S. inches closer to a direct military confrontation against Russia and, more recently, China. History does appear to be repeating itself. When the government of Bashar al Assad called on Moscow for assistance in fighting against the NATO-backed terrorists, it certainly was reminiscent of when the PDPA had done the same many years before. Thus far, the Syrian Arab Republic has continued to withstand the destabilization efforts carried out by the Al Qaeda-affiliated terrorist groups and Kurdish militias at the behest of the United States, and has not collapsed as Libya, Yugoslavia, and Afghanistan did.
But what often gets overlooked is the repeated Brzezinskist formula of funding highly reactionary forces and promoting them as “revolutionaries” to Western audiences in order to fight governments that defy the global dictatorship of the United States and refuse to allow the West to exploit their natural resources and labour power. As Karl Marx once said, “Men make their own history, but they do not make it as they please; they do not make it under self-selected circumstances, but under circumstances existing already, given and transmitted from the past.” Such a phenomenon is no accident or a mere mistake. The geopolitical instability that followed after the overthrow of the PDPA ensures that no sound, united, and formidable opposition against U.S. imperialism will emerge for an indefinite number of years; and it seems that Libya, where the Brzezinskist-style of regime change also saw success and which is now a hotbed for the slave trade, is on the same path as Afghanistan. This is all a part of what Lenin calls moribund capitalism when he discussed the economic essence of imperialism; and by that, he meant that imperialism carries the contradictions of capitalism to the extreme limit. American global monopoly had grown out of U.S. foreign policy, and it should go without saying that the American Empire cannot tolerate losing its Dollar Supremacy, especially when the global rate of profit is falling. And if too many nations reject U.S. efforts to infiltrate their markets and force foreign finance capital exports onto their economies in order to gain a monopoly over the resources, as well as to exploit the labour of their working people, it would surely spell a sharp decline in American Dollar hegemony. The fact that the United States was willing to go as far as to back mercenaries to attack the former Democratic Republic of Afghanistan and fight the Soviet Union, as well as to spend billions of dollars on a highly elaborate but effective propaganda campaign, shows a sign of desperation of the American Empire in maintaining its global hegemony.
Since the end of World War II the United States has been, and is by and large still, the overwhelming world-dominating power. It is true that the American Empire is in decline, in light of increasing trends towards “de-Dollarization,” as well as the rise of China and Russia which pose as challenges to U.S. interests. Naturally, Washington will desperately try to cling on to its number one position in the world by accelerating the growth of its global monopolies — whether it is through placing wholly unnecessary tariffs against competitors such as China, or threatening to completely cut Venezuelan and Iranian oil out of the global market — even if it means an increasing drive towards World War III. The current global economic order which Washington elites have been instrumental in shaping over the past several decades reflects the interests of the global capitalist class to such an extent that the working class is threatened with yet another world war despite the unimaginable carnage witnessed during the first two.
When we look back at these historical events to help make sense of the present, we see how powerful mass media can be and how it is used as a tool of U.S. foreign policy to manipulate and control public opinion. Foreign policy is about the economic relationships between countries. Key to understanding how U.S. imperialism functions is in its foreign policy and how it carries it out — which adds up to plundering from relatively small or poorer nations more than a share of wealth and resources that can be normally produced in common commercial exchanges, forcing them to be indebted; and if any of them resist, then they will almost certainly be subjected to military threats.
With the great wealth that allowed it to build a military that can “project forces over long distances,” the United States is in a unique position in history, to say the least. However, as we have seen above, the now four decade-long war on Afghanistan was not only fought on a military front considering the psy-ops and the propaganda involved. If anything, the Soviet Union lost on the propaganda front in the end.
From Afghanistan we learn not only of the origins of Al Qaeda, to which the boom in the opioid-addiction epidemic has ties, or why today we have the phenomenon of an anti-Russia Western “left” that parrots imperialist propaganda and seems very eager to see that piece of Cold War history repeat itself in Syria. We also learn that we cannot de-link the events of the 2001 direct U.S. military intervention in Afghanistan and what followed from those of 1979; Afghanistan’s colonial-feudal past, its break from that with the 1978 Saur Revolution, and the U.S.-led Mujahideen are all as much of a part of its history (and the Greater Middle East, by extension) as the events of 2001. It cannot be stressed enough that it is those historical conditions, particularly as they relate to U.S. foreign policy, that helped to shape the ongoing conflict today.
Obviously, we cannot undo the past. It is not in the interests of the working class anywhere, in the Global South or in the Global North, to see a third world war happen, as such a war would have catastrophic consequences for everyone — in fact, it could potentially destroy all of humanity. Building a new and revitalized anti-war movement in the imperialist nations is a given, but it also requires a more sophisticated understanding of U.S. foreign policy. Without historical context, Western mass media will continue to go unchallenged, weaning audiences on a steady diet of “moderate rebels” propaganda and effectively silencing the victims of imperialism. It is necessary to unite workers across the whole world according to their shared interests in order to effectively fight and defeat imperialism and to establish a just, egalitarian, and sustainable world under socialism. Teaching the working class everywhere the real history of such conflicts as the one in Afghanistan is an important part of developing the revolutionary consciousness necessary to build a strong global revolutionary movement against imperialism.
Originally published on 2019-03-30
About the author: Janelle Velina is a Toronto-based political analyst, writer, and an editor and frequent contributor for New-Power.org and LLCO.org. She also has a blog at geopoliticaloutlook.blogspot.com.
Source: LLCO.org
Origins of images: Facebook, Twitter, Wikimedia, Wikipedia, Flickr, Google, Imageinjection, Public Domain & Pinterest.
Read our Disclaimer/Legal Statement!
Donate to Support Us
We would like to ask you to consider a small donation to help our team keep working. We accept no advertising and rely only on you, our readers, to keep us digging the truth on history, global politics and international relations.
[wpedon id=”4696″ align=”left”]
FOLLOW US ON OUR SOCIAL PLATFORMS